How to Install Kali Linux on VMware VM. Kali is a free Debian-based Linux distribution intended for penetration testing. The first version of Kali Linux was released in 2013 as the rebuild of BackTrack Linux – a previous well-known distribution for security auditing and penetration testing. This wikiHow teaches you how to install and use the VirtualBox application on your Windows, Mac, or Linux computer. VirtualBox is a program which emulates a second computer, allowing you to install and use operating systems (e.g., Windows 7) on VirtualBox without having to change your computer's actual operating system.
- Kali Linux For Oracle Virtualbox
- How To Install Kali Linux On Virtualbox Macbook
- Kali Linux Virtualbox Tutorial
- Install Kali Linux On Mac Using Virtualbox
Here you will find out:
In this video I will show you how to install Kali Linux version 2017.2 on a Mac Book Pro. Installation of Kali Linux on Mac using VirtualBox:- Open your VirtualBox application and click on the Virtual machine you created for Kali Linux. Click on Start at the top of the icon bar. A number of different boot options will appear. Kali’s virtualization support includes the ability to reside inside Linux virtual machines, pre-built ISO images for VMware, VirtualBox, Hyper-V, and Vagrant alongside support for containerization platforms Docker and LXC. So, you can install Kali Linux in any standard platform that relies on virtualization without facing additional hassles.
- Kali benefits on VirtualBox
- how to prepare for Linux Kali installation
- when DiskInternals can help you
Are you ready? Let's read!
Kali benefits on VirtualBox
Kali Linux is a Debian-based security testing program for virtualized environments that contains many tools and applications for network auditing.
Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox has many advantages:
- There is no need to reboot the computer if multiple operating systems are running at the same time.
- Running Kali Linux on a virtual machine takes place in an isolated environment, so it is as secure as possible.
- You can take a snapshot of the OS at any time and retrieve at a later time. This makes the VM less vulnerable.
- Copies of a VM configured with Kali Linux can be transferred to other computers.
Kali Linux For Oracle Virtualbox
- Thanks to the USB VirtualBox pass-through function, you can connect any physical USB device directly to the virtual machine.
Preparing for Linux Kali installation
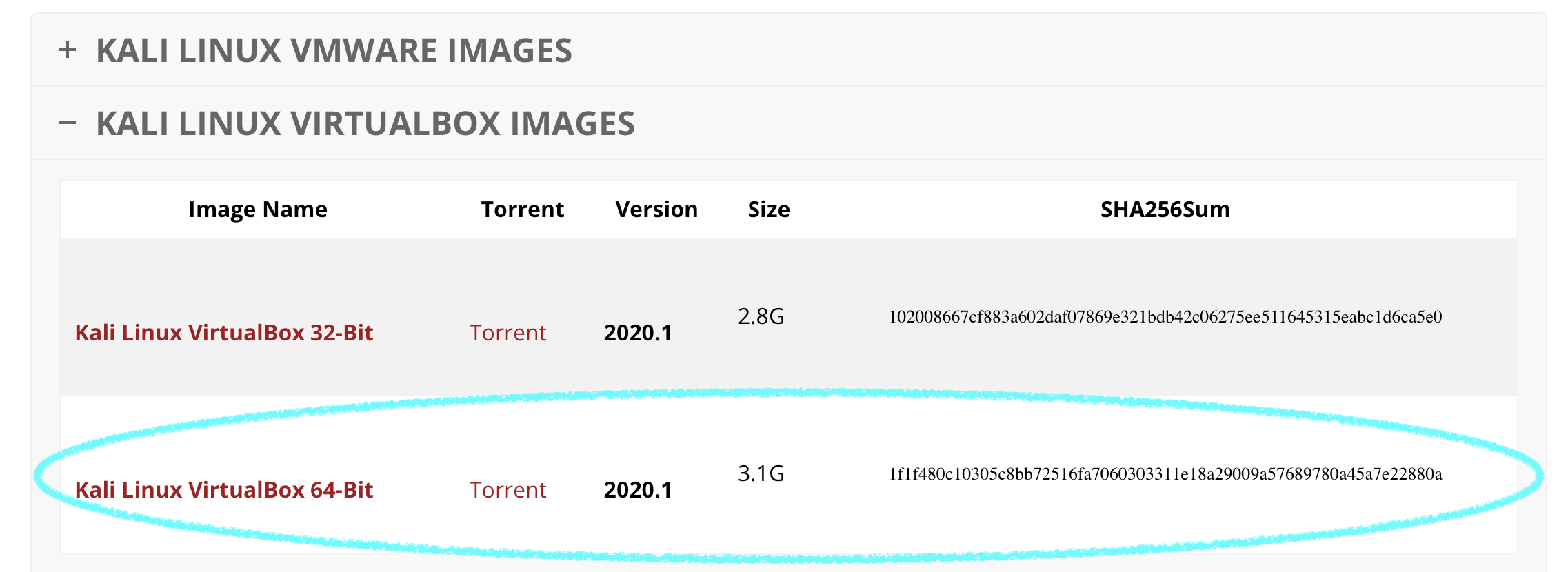
First, download the Kali Linux ISO from the official website. You have a wide variety of ISO images to choose from: both 32-bit and 64-bit images, which can come with different user interfaces (XFCE, Gnome, KDE, LXDE, etc.). You can download images via HTTP or via Torrent protocols. Be sure to save the downloaded file in a custom folder. Here’s an example file path: C:VirtualBoxkali-linux-2020.1-amd64.iso.
Check the SHA256 checksum to ensure the image is consistent after the download is complete.
Step 1. Create a new VM in Kali
To continue installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox, you will need to create a new VM.
To do this, open VirtualBox, click on the Machine button, and then on the Create button.
Next, enter the basic parameters. Here's an example of what information you’ll enter:
Name: Kali Linux x64
Machine folder: E:VirtualVirtualBox (it is not recommended to use the system partition for storing virtual machines)
Type: Linux
Version: Debian * 64
Memory size: at least 4096 MB
Hard disk: Create and configure a new hard disk, as well as set the location of the virtual disk file; for example: C:VirtualVirtualBox Kali Linux_x64.vdi
The virtual disk files are usually saved in the default VM folder.

The virtual disk file size must be at least 20 GB and the hard disk file type must be VDI.
Physical disk storage: dynamic
Now you just have to click on the Create button to complete this process.
After that, additional parameters of the new VM will become available to you, which you can change if you wish.
Step 2. Launch Kali Linux on VirtualBox
Boot from the virtual DVD and, in the Boot Options menu for Kali Linux, select the graphical installation. Select the language, location, keyboard layout and other criteria. You will also need to set up your network, domain name, passwords, clock, etc.
Next, partition the disk; if this is your first time, select the Use entire disk option. In this case, confirm the deletion of data from this disk. Now decide how much of the disk will be allocated to each partition. You can select the All files option in one section. When you are done, click on the Finish partitioning button.
Next, configure the package manager. This is where the network mirror option should be activated, which will allow you to update application packages from online software repositories.
Next, provide information about the proxy server. If you are not using it, just click Next.
You will then be prompted to install the GRUB boot loader to your hard drive. Click the Yes button and complete the installation. Then restart your computer and you will see the Kali Linux login screen. Enter your username (root) and password and you will be taken to your Kali Linux desktop.
Step 3. Deploy OVA Template Kali on VirtualBox
This method of installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox is much easier, as most of the settings are already enabled by default. Go to the official Offensive Security website and download the appropriate OVA template, such as the 64-bit Kali Linux VirtualBox OVA image.
Now go to VirtualBox and open Tools. Here, select the Import tab and you will see the VA Import Wizard. Select the main suggested VM parameters (the default virtual machine name is “Kali-Linux-2020.2-vbox-amd64” in this example). Next, define the directory where the virtual machine will be deployed from the template and select 'Create new MAC addresses for all network adapters'.
Next, enable the function Import hard drives as VDI. Wait for the import to complete and select the Kali virtual machine deployed on VirtualBox in the template. Now click on Start. Enter your username (root) and password and press Enter. You are now on the Kali Linux desktop.
Use VMFS Recovery for VM data safety
If there is something wrong with your virtual machine (if .vmdk files are missing or deleted), you can restore them and rebuild the virtual machine using DiskInternals VMFS Recovery.
The application immediately recovers VMFS disks stored on damaged or inaccessible hard drives. Every step of the process is supported by the Recovery Wizard, so it's unrealistic to make a mistake when recovering data. Virtual disks can be mounted as local disks, and are accessible from Windows Explorer. All Windows restrictions are bypassed by the recovery process. When you view the recovered data for free and make sure it is in place, purchase a license to access files or export selected files. It doesn't take long, and the result will pleasantly surprise you.
In addition, by purchasing a license, you receive not only the ability to do unlimited exports, but also round-the-clock and year-round technical assistance from the company.
FREE DOWNLOADVer 4.8, WinBUY NOWFrom $699
- VMFS Recovery
- Enabling SSH
- Remote Recovery
- Recovery Guide in Pictures
- Export to: Virtual Disks, FTP
- File Preview
- RAID, Dynamic Hard Disks
- Power Search
- Create Disk Image
 1 reviewsRelated articles
1 reviewsRelated articles- How to Fix/Repair Corrupted VMDK Files Effortless
- Mounting Hard Drives (vmdk files) of a Virtual Machine Running on a ESX Server
- Mounting Server Disks
- Recover Deleted VMDK from Datastore Today
- repair VMDK files in VMware | DiskInternals VMFS Recovery™
- VMFS Recovery™ for VMware Data Recovery
- Recover VM from flat VMDK - The Best Solutions
- Restore a VMDK file
- Is VMware virtual machine inaccessible? Fix it!
- Restore VMware virtual machine from VMDK file
- Restore VMware VM with snapshot(delta.vmdk) files
- VMFS Recovery software as a solution for NFS data repair
- VMware vs Hyper-V Comparison
- What is ESXi Recovery Mode
- VMware RAW Device Mapping and File Recovery
- Difference between ESX vs ESXi
- Virtualization technology: what is it and how does it work?
- VMware vMotion: all you need to know
- VMware: clone and data recovery
- What is VMware HA?
- What is the difference between VMware HA vs vMotion
- VMware vMotion storage: What do You Need to Know
- What is VMware DRS?
- VMware Fault Tolerance: what is it and how does it work?
- VMFS Block Size: How to Choose
- VMFS UNMAP: What is It?
- What is Space Reclamation and How to Perform It
- What is Thin Provisioning?
- Thick vs Thin Provisioning: All You Wanted to Know
- iSCSI LUN and Data Recovery
- How to Upgrade VMFS from 3 to 5th version
- VMkernel and Its Interactions with Storage
- VMware Infrastructure: What Components are Used
- VMware vMotion requirements: for VMs and for hosts
- What is VMware vCloud Suite
- VMware vMotion vs storage vMotion: all you wanted to know
- VMware FT vs VMware HA: what the difference?
- VMware Template vs VMware Clone: the differences and common
- VMware Workstation and Its Uses
- What is VMware VDS and How It Works
- ESX Partitions: All You Wanted to Know
- VMkernel Ports and Networking Layers
- What is VMware vSphere
- VMware Cold and Hot Migration: What Is It
- What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure(VDI)?
- What is VMware vCenter Server and How Does It Works
- What is VM Host Server
- The importance of snapshots in VMWare
- How to Manage VMware ESXi
- What is vVol and How Does That Work
- Find Your Reason for a Virtual Machine Usage
- What is VMware vSphere and vCenter
- What is NVRAM? Are these files important?
- What is a VM Cluster and How to Create It
- Virtualization: How Does It Work?
- VMware Content Library: What Is It and How Does It Work
- VMware vs VirtualBox: What Is The Difference
- VirtualBox: 'No bootable medium found' issue
- Comparison VDI vs Citrix
- VM: Hyper-V Integrated Services
- Hyper-V Checkpoint and Its Importance for VM
- 3-2-1 Backup Strategy for Data Safety
- Hyper-V Export VM: How Does It Work
- ESXi Free Limitations: Pros and Cons
- Convert VMware to Hyper-V Fast and Safe
- Hyper-V Networking: How to Manage It
- VMware: Workstation Pro vs Workstation Player
- Convert VHD to VMDK
- What is Hyper-V USB Passthrough
- What is Hyper-V VDI and Its Benefits
- How to Use VirtualBox Correctly
- P2V vs VMware: What is Better for You?
- How to Install Kali Linux VMware
- How to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox
- VMware ESXi Root and Default Password
- What is VMware networking?
- VHDX Files and How to Mount Them on Windows
- What is Asynchronous Replication
- Disaster Recovery Checklist: You Need A Plan
- VMware vSwitch
- How to open VMDK files
- VMware Network Adapter settings
- VMware EVC Mode
- VMware NFS vs VMFS
- VMware snapshot best practices
- Hyper-V Virtual SAN
- Hyper-V NIC Teaming
- NSX-T and NSX-v
- AWS EBS Snapshots
- Hyper-V Nested Virtualization
- About VirtualBox full screen
- About VirtualBox network settings
- About VMware home lab
- Install VirtualBox Extension Pack
- Physical and virtual servers
- VMware Player and VMware Workstation
- Thick and thin provisioning
- Install ESXi from a USB
- Steps to update VirtualBox
- Update ESXi
- Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox
- ESXCLI commands
- Remote control an Ubuntu
- Setting up VirtualBox
- Create a Virtual Machine
- VMware vSphere 7
- VMware vSphere Replication
- About vSphere Web Client
- About VMware Data Protection
- About VMware Host Profile
- About VMware vRealize Orchestrator
- The VM session was closed before any attempt to power it on: error code 0x80004005
- Intel VT-x in BIOS: how to enable it?
- Want to increase VirtualBox disk size? Here is a guide on how to do it safely!
- VMware Cloud Foundation
- VMware Horizon and its components
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and VMware Horizon
- The comparison of Citrix and VMware
EFS Recovery - repair your EFS files from damaged or formatted disks
Acсess Recovery - make your .mdb and .accdb files readable again
RAID Data Recovery - make your RAID arrays alive
Recover a Partition - an expert at recovering lost partitions
What are VMware®, VMFS, VMDK and ESX Server?VMware® is one of the most comprehensive virtualization systems allowing users to run multiple instances of desktop or server operating systems on a single physical PC. Desktop and server versions of VMware® are available. The desktop edition runs on top of an existing system (e.g. Windows, Linux etc.), while VMware® ESX Server™ is a dedicated operating system that can host multiple virtual PCs without requiring a host OS.
VMware® ESX Server™ uses its proprietary file system called VMFS to format a physical partition on a hard drive. Virtual disk images representing these virtual PCs are stored on VMFS partitions as files in VMDK format.
VMFS Recovery™ is the first commercially available independent product to read and recover VMFS-formatted disks.
VMFS Recovery™RAID Recovery™Partition RecoveryUneraser™NTFS RecoveryEFS Recovery™DVR RecoveryIn this article and video, I will show you how to install Kali Linux 2020.1 on VirtualBox. Also, install a single boot with Kali Linux. I will cover some big changes that have been made with this new release.
“Kali Linux is an Advanced Penetration Testing Linux distribution used for Penetration Testing, Ethical Hacking and network security assessments.”
Kali Linux 2020.1 Release
On 28 January 2020, Kali has kicked off with the first release of the decade, Kali Linux 2020.1 In this article I will cover the most important changes.
Non-Root
The default credentials have been root/toor. This is no more. Kali Linux is no longer using the superuser account, root as default in Kali 2020.1. The default user account is now a standard, unprivileged, user.
root/toor is dead. Long live kali/kali
Use Kali Linux as your Main OS?
How To Install Kali Linux On Virtualbox Macbook
Now you can use Kali Linux as your main OS, but should you? This is up to you. There wasn’t anything really stopping you before, but Kali isn’t encouraging it. They still don’t. Therefore this is only recommended for people who are familiar with Kali enough.
Kali-Undercover
Kali Linux continues with Undercover. Kali-undercover now starts to feel even more like Windows to help blend in.
How to enable the undercover mode in Kali Linux:
Kali Single Installer Image
Kali Linux does not longer offer separate images for every desktop environment (DE). Instead, they have a single image with the option to pick your DE during installation. This means there isn’t a download link for Xfce, GNOME, KDE, MATE or LXDE DEs anymore. Just one image to rule them all.
At the install time, you may select the tools included with Kali (or none at all)! This gives you more control over what you want. Now you can install Kali without any meta-packages, giving a bare Kali installation, you can individually select what tools you want (rather than groups). More Info
Note: “Kali Live” is not included in this image. If you wish to use live mode, you’ll need the live image.
Use the space bar to check the options that you want to choose
Short keyboard explanation for “noobs” beginners ;-)
On the keyboard image below you can see the options that are used with the installation of Kali Linux.
Install Kali Linux
This step-by-step tutorial teaches you to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox.
Download Kali Linux
I would like to make another note. Personally, I always download every ISO from the original OS and certainly NO pre-made ones. Especially when it comes to Kali Linux. This is because of possible vulnerabilities.
First, you have to download the ISO file from the official Kali website. This is because, in this article and video, I choose the Kali Linux 64-Bit (Installer)
Kali Linux Download
Kali Linux Download
You can download VirtualBox here. How to download and install the VirtualBox on your Linux or Windows, I will cover that soon in a new article.
At the bottom of this article, you can watch a video of the entire Kali Linux installation.
Or click on this link to go to the video on YouTube.
Install Kali on VirtualBox
Now the download is complete, open VirtualBox and click on “New”
This will open a new screen. Give it the name “Kali Linux 2020.1” And choose the type: “Linux” and “Debian”. (Kali Linux = Debian Based). Or whatever you may use. Maybe you even use another Linux distro
After that click on “Next”
Memory size
Set at least 1 GB of RAM. “If your physical machine is 16 GB of RAM, you can set 4 GB of RAM for a virtual machine to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox.”
Personally I always set the memory size to 2 GB RAM. This is because most (when I run some tests) I have more than one Virtual Machine (VM) open.
After that click on “Next”
Hard disk
Put it on: “Create a virtual hard disk now”
And click on “Create”
Create virtual hard disk
Click on VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)
Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Storage on physical hard disk
The advantage of a dynamically allocated hard disk file is, that as the file gets larger because then it adapts to the size of the file.
“Next”
File location and size
For the install of Kali, you really need a minimal of 20 GB. In this example, I put the size to 50 GB +.
Click on “Create”
It is always good to take a generous amount of space. Better too much than too little, and you will get into trouble. Some tools or programs simply need space.
At the bottom of this article, you can watch a video of the entire Kali Linux installation.
Or click on this link to go to YouTube.
Now that the install on VirtualBox is ready so far, we are going to adjust some settings.
Click On “Settings”
Storage
Click on storage - Empty
Choose a Disk File
To select On the Disk File, click on the box that I made red next to “Optical Drive”
Then choose the Kali Linux ISO that you just downloaded.
Network
Select Network and select “Enable Network Adapter” This is usually already checked.
Select Attached to: “Bridged Adapter”. Why… There is a very simple reason for this: the default network. … Because by selecting the Bridged Adapter, your guest operating system will work on the same network as does your host. And choose wlan0
And click on “✓ OK”
There are many more options you can click and adjust. You should look for the best options for yourself.
The best thing about using a virtual environment is that you can and may make mistakes, because, you only learn from this. You just start again if it goes wrong.
Install Kali On VirtualBox
When you have adjusted all settings, it is time to install Kali Linux on your VirtualBox.
Select start-up disk
As soon as you have clicked on “Start” a new window will open. We will continue from here. Choose the correct ISO and click on “Start”
Select the correct installation
For this installation, I choose the regular “Install”, Instead of the Graphical install.
I will show both options in the Video. At the end of the video, you can see the graphical installation (in short).
Choose the lanuage for the install process
We will of course do this in English :)
Select your location
Select your location. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Configure the keyboard that you will use
Depending on the Language and region, you can choose your keyboard. For this install, I choose the default American - English.
Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.

Choose a hostname for this system
As you can read on the screen, the hostname shows the identification from your system to your network. You can choose what you like. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Choose your domain name
I leave this open. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Setup user
Choose a user name. As you can read above, with the new Kali Linux the root user is no longer standard. Click on “enter”
“root/toor is dead. Long live kali/kali”
Usermame for the new account
Choose a password for the new user
Re-enter the password to verify
Select your time zone
Partition disk
For this Kali Linux install we use the “Use entire disk and set up encrypted LVM” So that during the start-up of Kali you are prompted for a password … “We like to be safe” Then click “enter”
Select disk to partition
Choose the correct disk that you want to use. Nothing for me to do here so “enter”
Partition scheme
Here we choose “All files in one partition, recommended for new users”. - “enter”
Write the changes to disk and configure LVM
Use the tab to jump to “Yes”.
Click on “enter”

Eresing data
Take a coffee, because this will take some time.
“The installer is now overwriting SCS12 (0,0,0), partition (sda) with random data to prevent meta-information leaks from the encrypted volume. Canceling this action, albeit at the expense of a slight reduction of the quality of the encryption”
Encryption passphrase
This took a while for this installation.
Choose a password for the encryption and click on “enter”
Re-enter the password
Amount of volume group to use for guided partitioning. In this example, I use all because this is a virtue environment. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Overview configure partitions and mount points
Write changes to disk
Use the tab to go to yes. Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Install the base system
Configure the package
We don’t need an HTTP proxy, so we leave it empty. (blank). Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Choose software to Install
* Select all the options that you want to install for your Kali Linux installation
* Use the space bar to select the option. With the arrow on your keyboard for up or down.
* With this install I opted for:
* Kali desktop environment
* xfce
* Generic metapackages (kali-linux-*) I did installed the default. Enough choice for you.
✓ Standard system utilities (All the way at the bottom)
Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further. This takes some time to install. Grab yourself a coffee.
Use the space bar to check the options that you want to choose
The GRUB boot loader
We certainly want to install the GRUB boot loader, so choose <Yes> Click on “enter” on your keyboard to go further.
Kali Linux Virtualbox Tutorial
Device for bootloader installation
Installation is complete, time to boot your system
Finally, the install of the Kali Linux install is complete. Press “enter” for a reboot.
Kali after the install
Unlock disk
You have your file encrypted because of more security. Use your password to unlock the disk.
Enter your user name and password
Finally, the Kali Linux installation is successful.
A nice article to continue reading. “Best Linux Commands Hacks and other Cool Tricks for Beginners”
At the bottom of this article, you can watch a video of the entire Kali Linux installation.
Or click on this link to go to the video on YouTube.
Single Boot Kali
Installing Kali Linux on your computer is an easy process. First of all, you’ll need compatible computer hardware. Kali is supported on i386, amd64, and ARM (both armel and armhf) platforms. The hardware requirements are minimal as listed below, although better hardware will naturally provide better performance. The i386 images have a default PAE kernel, so you can run them on systems with over 4GB of RAM. Download Kali Linux and either burn the ISO to DVD or prepare a USB stick with Kali Linux Live as the installation medium. If you do not have a DVD drive or USB port on your computer, check out the Kali Linux Network Install.
Installation Prerequisites
- A minimum of 20 GB disk space for the Kali Linux install.
- RAM for i386 and amd64 architectures, minimum: 1GB, Recommended: 2GB or more.
- CD-DVD Drive / USB boot support
Preparing for the Installation
- Download Kali Linux.
- Burn The Kali Linux ISO to DVD or Image Kali Linux Live to USB.
- Ensure that your computer is set to boot from CD / USB in your BIOS.
Install the ISO to USB Linux command line
Put your USB stick in your computer and give the command “fdisk -l” to “List the partition tables for the specified devices and then exit”
Make sure the USB is unmouted:
Use the command below to write your ISO to your USB
Video
In this video, I show you how to install Kali Linux on a “normal Install” Because, the install of Kali Linux is a long process, I shortened the video a bit. At 17.20 minutes in the video, the graphical install starts.
Become a member on Odysee.com
Earning on Odysee for watching videos ♥️
Here an invitation link, so that we both benefit.
In this way, you also support my work.
Conclusion
The latest Kali Linux 2020.1 install has really surprised me because it offers an impressively rich set of tools for almost every phase of the penetration testing process, the final choice of tools to use will always depend on the tasks and goals of your current project. What for many “hackers”, pen-testers and cybersecurity engineers should be added on Kali are a number of programming options because (some) hackers like to program.
Just remember, Performing any hacks without written permission is illegal ..! Read also the Disclaimer..!
WANT TO SUPPORT THE WEBSITE
Dear people, I do a lot of things on the Internet and I do it all for free. If I don’t get enough to support myself, it becomes very difficult to maintain my web presence, which takes a lot of time, and the server costs also have to be paid.Your support is greatly appreciated.
Install Kali Linux On Mac Using Virtualbox
Thanks guys ..!
Use the link above to donate via PayPal.
IMPORTANT THINGS TO REMEMBER
✓ This Video and Article is made for educational purposes and pentest only.
✓ You will not misuse the information to gain unauthorized access.
✓ This information shall only be used to expand knowledge and not for causing malicious or damaging attacks…!
Read also the Disclaimer
All the techniques provided in the tutorials on HackingPassion.com, are meant for educational purposes only.
If you are using any of those techniques for illegal purposes, HackingPassion.com can’t be held responsible for possible lawful consequences.
My goal is to educate people and increase awareness by exposing methods used by real black-hat hackers and show how to secure systems from these hackers.
Finally
If you have any questions about this article, any feedback, suggestions if you want to share your thoughts, contact me. Please feel free to do so.
